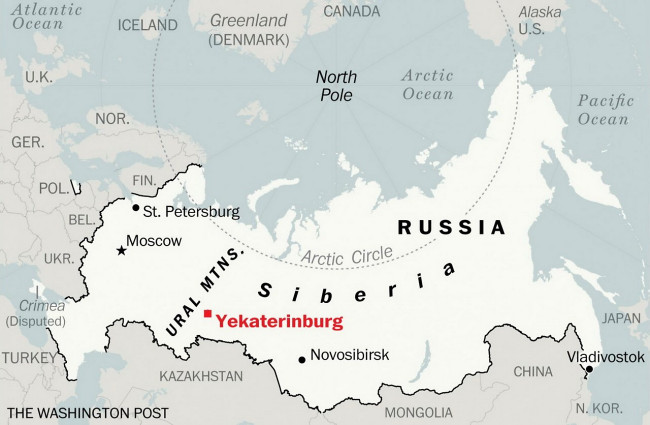
Is Dyatlov Pass in Siberia?
YEKATERINBURG, Russia — Where is Siberia?
By David Filipov / The Washington Post
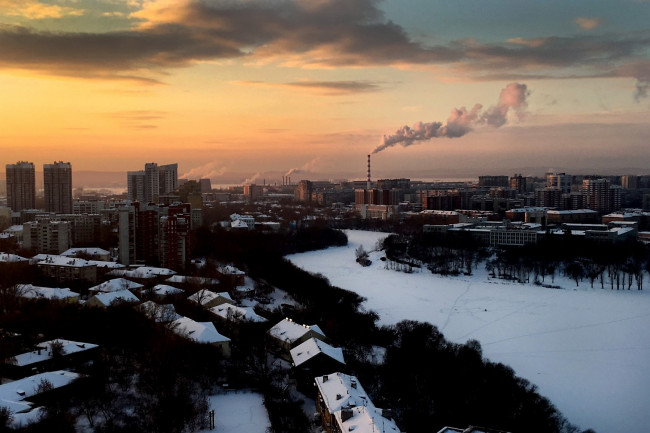
The Ural Mountains are nowhere to be seen in Russia’s fourth-largest city, which sits to the east of the ridge that divides Europe and Asia. But this city considers itself the capital of the Urals, and not a part of Siberia.
You know the place: bears, vodka, oil, very big, awfully remote, once filled with political prisoners (and now home to some of Russia’s cutting-edge computer geniuses).
But where does it start?
Encyclopaedia Britannica, for one, describes it as that vast region of Russia "that extends from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east." That’s not quite right. At least not from the point of view of the 1.3 million residents of Yekaterinburg, Russia’s fourth-largest city, which sits just to the east of the range that divides Europe and Asia. Yekaterinburgers will tell you with tightly clenched teeth that they are in the Urals. Not. Siberia. I ran into this when I wrote a blog post about a "Siberian bar" in Yekaterinburg that had come up with humorous Russian translations for American cocktails. Facebook shuddered with the umbrage of Uralites (and I corrected the wording).
But no one could say for sure where Siberia does start. So I traveled to Yekaterinburg to find out, and this became a local news story. A camera crew from Malina.am, a Yekaterinburg television and news website, followed me around, trying to help explain the difference between Siberian and Urals culture.
Siberia gets way more news coverage because it’s huge, comprising 74 percent of Russia’s land mass, according to Olga Guryevskikh, who teaches geography at the Ural State Pedagogical University. The Urals make up just 6 percent, but the region is also a famous brand — check the price of oil futures.
With that in mind, I made my first stop at a restaurant called Pelmeni Club, whose co-owner, Yelena Makusheva, served tasty samples of dumplings from Siberia and the Urals. The Siberian ones had exotic, frontier-sounding names such as "Yamal Wild Deer" (with real deer meat) and “Grandmother in a Kerchief" (beef, pork and mutton). The Urals pelmeni were called "Duck and Goose" and "Turnips With Mushrooms."
They all tasted good. Which ones did Makusheva prefer? And what did they say about regional cultures?
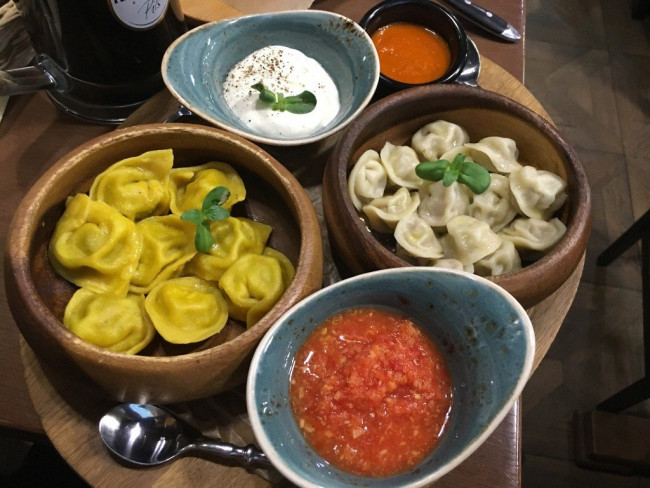

One way to tell the difference between Siberia and the Urals is with pelmeni dumplings. The yellow ones on the left, made with carrots, duck and goose, are from the Urals. The ones on the right, pork, beef, and mutton, are from Siberia.
"There is no better or worse," she said, smiling. "Siberian, Urals, we’re all Russians. The pelmeni are the best wherever we are."
This last could’ve been a philosophical statement, or it could’ve been a plug for the restaurant she and her partner have opened in the Siberian city of Tyumen. It was time to do an interview at the Malina.am TV studio.
The host, Olga Chebykina, brought in Guryevskikh, who took out a topographical map of Russia and, as the cameras rolled, pointed at the yellow section that indicated the Ural Mountains. On the map, that yellow yields to a sea of green that stretches east. Even though you can’t see the mountains in Yekaterinburg, the city is on the yellow part of the map. The green sea is Siberia.
Maddeningly, that boundary did not match modern regional borders.
I resolved to find that magical spot.
"You might be able to find the physical border," Chebykina said. "But the border in the soul is hard to define."
More mystery!
– 2 –
Marina Tchebotaeva, the down-to-earth general director of the Yekaterinburg office of a German water treatment company, tried to explain. The Urals, generally speaking, are populated by descendants of peasants who toiled at factories in the 18th century, when Peter the Great needed iron and copper to fight his wars, she said.
"The main characteristic of Uralites is the love of work,” Tchebotaeva said. “We have a lot of large factories, good engineers, and we really love to work and get good results."
Siberia, on the other hand, was populated by explorers and pioneers, she said — Cossacks who built forts, and the traders and farmers who settled near them. "Siberians have always been brave, freedom-loving and enterprising people," she said. "They’ll never leave you by the side of the road. If your car breaks down, they’ll help you. Because if you’re stuck on the side of the road when it’s 22-below, you’ll never survive."
As she said this, the temperature outside was descending along with the weak, winter sun. It would hit 22 degrees below zero that night.
"Urals people wouldn’t leave you, either," Tchebotaeva added.
Tchebotaeva posted on her Facebook page about my quest, prompting reactions that aptly describe the state of U.S.-Russian relations.
"Why does he need to know?" read one post. "Maybe he’s trying to divide the country!"
Another poster elaborated on this theory. The United States "is going to try to separate Siberia from Russia."
It sounds overwrought, but try to imagine an expedition of Russian reporters venturing into Colorado, purportedly to find where the Rockies end and the Midwest begins. Those would have to be spies looking for our missile silos, right?
Okay, maybe not.
The next morning, it was a dare-we-call-it-Siberian 13-below as we headed east from Yekaterinburg.
We passed fields and snow, and snowy fields. The sun rose and the temperature actually went down. The road was plowed, and Russia has excellent gas stations with well-stocked convenience stores.
And then, on a wooded upgrade about 200 miles east of Yekaterinburg, we found that mystical border, marked by a faded, primitive sign with the word "Siberia" scrawled on it, just past a bridge over the trickle of a brook fed by an underground spring. At the water’s edge, an inscription on a stone described this as the accepted border of Siberia in the 18th century. Nearby, a boarded-up cafe was surrounded by knee-deep, untouched snow, and a large, cinder-block outhouse loomed.
The magic of this place was faint, but the cold was not: My iPhone froze, as did the Malina.am crew’s drone.
A few miles into Siberia lay the town of Ust-Nitsinskoye, a settlement of a thousand souls founded in 1622 on the spot where the Nitsa River flows into the Tura River.
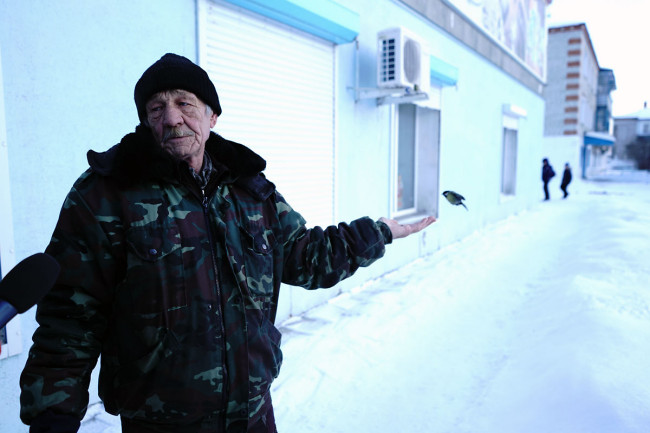
The appearance of TV cameras sent townspeople scurrying. The first who was willing to talk was a retired bauxite miner, Boris Mihaylovich, 65. He was wearing military fatigues and feeding chickadees out of his bare hand, seemingly oblivious to the chill. How very Siberian!
"What is the difference between people from the Urals and Siberians," asked Svetlana Smirnova, the Malina.am producer. "Is there any?"
"I don’t think so," Mihaylovich said.
Not too helpful.
The next person willing to speak to us gave only his nickname, Tolik.
"What’s the difference between people from the Urals and people from Siberia?" Smirnova asked.
"Uhm, I don’t know," Tolik said.
"You don’t notice a difference?" Smirnova persisted.
"Nope," said Tolik.
Smirnova is a good journalist. She didn’t give up.
"So are you closer to a Siberian or a Uralite?" she asked.
"I’m a little bit of both," Tolik shrugged.
Here, the search ended. It was dark, and freezing, and 200 miles back to Yekaterinburg.
Some of it in Siberia, the rest in the Urals.
Whatever that meant.
Which way is Siberia? The answer is harder than you think.
The Washington Post's Moscow bureau chief, David Filipov, goes looking for Siberia.





