Controversy: FAQs and Myths
- Do Otorten and Kholat Syakhl really mean "Don't Go There" and "Mountain of the Dead"?
- What does Mansi mean?
- Why the group pitched their tent at this spot on the night of the incident
- How steep was the slope where the tent was pitched
- More questions about the tent
- Tent layout
- Labaz (cache)
- Skis
- Mansi chum
- The group had one ice axe yet two were found
- Why the livor mortis spots did not match the position of some bodies?
- Maps with the ravine and den where Dubinina, Kolevatov, Thibeaux-Brignolle and Zolotaryov were found
- Passports
- Money
- Knives
- Who's burnt jacket is Slobodin posing with?
- Notorious frame №34
- Radioactive contamination on hikers clothes
- "Now we know snowmen exist"
- What happened to the original paper Evening Otorten?
- Where there burned trees in the area?
- Was there "skin found on the bark of the cedar"?
- Time of death
- How many cameras did Yudin say there were
- Who did Yudin give his vest that was found on Dyatlov
- Was Semyon wearing Lyuda's clothes?
- Where some cameras/films taken from the tent by members of the search party?
- Zolotaryov's camera
- Dogs
- Is it true that local people were not allowed to graze their animals in the area?
- Were hikers banned from going to the area after the incident?
- Histological analysis results of the first five bodies never made it to the case files
- Yudin recalls soldiers wrap [puttee] (rus. солдатская обмотка) that didn't belobg to the Dyatlov group
- The address of Dyatlov Pass is Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia, 624575 Google maps →
- Locations of Mihaylovskoe and Ivanovskoe cemeteries. Funerals →
Do Otorten and Kholat Syakhl realy mean "Don't Go There" and "Mountain of the Dead"?
Theory 1
Kholat Syakhl is called by Mansi "Mountain of the Dead" because legend goes nine Mansi hunters died mysteriously there. Others say they disappeared altogether.
Mount Otorten is called "Don't Go There" because these mountains, especially the "gates" between them are considered sacred and dangerous since ancient times.
Theory 2
Kholat Syakhl is marked on the maps as Peak 1079. Mansi Холат-Сяхыл, Холе-Чахль, Холат-Сяхль, Холат-Сяхл, Холатсяхыл, Солатчахл. Kholat (Холат) means "meager", "lack of game", "dead", Сяхль (Syakhl) means "mountain". The Mansi word kholat (холат) is a relatively common name on their territory and is part of at least 3 other topographic objects.
Отортэн is the distorted name of Вот-Тар-тан-Сяхыл (Mt Vot-Tar-tan-Syakhyl) meaning "Mountain that blows the wind" or "Mountain from which the wind blows". The Mansi emphasize that the winds very often blow from the side of this mountain (A.K. Matveev "The Peaks of the Stone Belt" 1990). Peak with this name is located several kilometers to the north and is inferior in height to what we know as Mt Otorten. Mansi have a different name for Otorten, Лунт-Хусап (Lunt-Khusap) meaning "Goose Nest" or Лунт-Хусап-Сяхыл (Lunt-Khusap-Syakhyl) meaning "Goose Nest Mountain". There is a Mansi legend that after the global flood, one goose survived on the peak of this mountain. The lake with the same name is located at the foot of the steep southeast slope of Mt Otorten. The lake with the same name is located at the foot of the steep southeast slope of Mount Otorten. It is from Lunt-Khusap-Tur Lake ("Goose Nest Lake") that the Lozva River originates.
What does Mansi mean?
Theory 1
"Forest dweller"
Theory 2
In fact, Mansi means "human being" and in an older Praugorian language a similar word is used for "man".
Why the group pitched their tent at this spot on the night of the incident
Theory 1
On January 31, the group arrived at the edge of a highland area and began to prepare for climbing. In a wooded valley they cached surplus food and equipment that would be used for the trip back. The following day (February 1), the hikers started to move through the pass. It seems they planned to get over the pass and make camp for the next night on the opposite side, but because of worsening weather conditions–snowstorms and decreasing visibility–they lost their direction and deviated west, up towards the top of Kholat Syakhl. When they realized their mistake, the group decided to stop and set up camp there on the slope of the mountain, rather than moving 1.5 km (0.93 mi) downhill to a forested area which would have offered some shelter from the elements. Yudin, the lone survivor, postulated that "Dyatlov probably did not want to lose the altitude they had gained, or he decided to practice camping on the mountain slope."
Theory 2
It is judged, based on the weather information available, what had been written in their journals and on information about the group's progress by Yuri Yudin, that they would have reached the slopes of Kholat Syakhl sometime in the afternoon of 1 Feb. At that latitude and time of year sunset is 1658, so it can be reasonably assumed that they got to the point were they pitched tent 60 minutes or so before then in order to give them time to erect the tent in daylight. Their final destination was Mount Otorten, and it was not feasible for them to have continued on at night. We can never know precisely why Dyatlov ordered the tent pitched were he did, but I doubt it was because they were lost. They were in fact on the correct route to Otorten. Also, if they managed to find their way about 1,500m to the treeline in the dark and in some difficulty after leaving the tent in a panic, they why could they not find their way to the treeline in daylight, and in good order? It must be presumed, without evidence to the contrary, that Dyatlov had intended to pitch the tent on the slopes of Kholat Syakhl. It is of course speculation that this was to give the group an extra challenge. Another factor is that when dawn broke, their destination, Mount Otorten, would be visible from their tent. This, after a difficult journey, would be good for moral as they could see their destination. This of course is speculation, but I do not believe they were lost and bumbling about. And to re-iterate, if they were lost, why could they make it to the treeline in the dark in a panic, and not in daylight in good order.
How steep was the slope where the tent was pitched


Official protocol report on the Dyatlov group tent:
"Tent site is located on the North- eastern slope of mountain 1079 (Kholat Syakhl official term) meters at the mouth of river Auspiya. Tent site is located 300 meters from the top of the mountain 1079 with a slope of 30 °..."
Second read on the photos
Rescuers removed hikers belongings, folded the tent and carried them down the slope for the convenience of the subsequent evacuation. From beneath the tent they removed three pairs of skis, two of which were given to the hunters Moiseev and Mostovoy that were transporting the items and one pair was used to mark the location of Dyatlov and Kolmogorova's bodies. On the photos we can see captured this precise moment: the tent is completely disassembled and pushed to the side, out from under the skis of the hikers are removed, rescuers are moving down the slope.
The two people standing to the left are journalist Yuri Yarovoy and the prosecutor criminologist Lev Ivanov. This photo is especially valuable because it allows us to measure the steepness of the slope of the mountain Kholat Syakhl right where the tent was pitched.
The original photograph (above) is tilted to the left, but the standing straight figures of Yarovoy and Ivanov can be used as a reference points to straighten the photo and measure the slope which is only 15 degrees. This is not more than the angle of climbing for stairs and escalators.
More questions about the tent
What was the mode of closing of the tent - buttons (пуговицы), straps?
Some sources say that the tent was found fastened and only two of the lower buttons were unfastened. I can't find a document that says so. Found an interview with Slobtsov from 6 May 2015 which doesn't make it any clearer.
Case file says "From the left end of the tent there is a hole that serves as an entrance. This hole is formed by two non-sewn halves of the fabric and from the inside is creped with a white sheet." ("С левого торца палатки имеется отверстие, служащее дверью. Указаное отверстие образовано двумя не сшитыми половинками ткани и с внутренней стороны задрепировано белой простынью." Nothing more on the closing and how it was found, fastened (with what?) or not.
~ If Zolotaryov and Tibo went out to pee, saw something in the sky, Zolotaryov went back for his camera and called the rest to see the light show in the sky, that is why they were with no shoes and Tibo and Zolotrayov were wearing valenki. But if the tent was fastened, I don't see the perpetrators going in and bother to fasten the tent unless they spend time inside and didn't want to be cold, which is far fetched.
Answer:
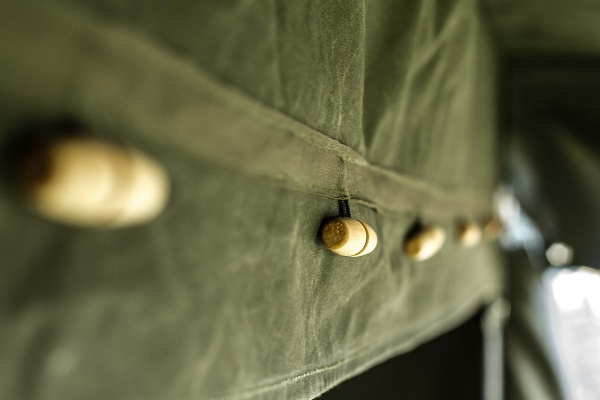
The only reliable fact is that the tent had buttons, but special ones - wooden toggles (клеванты).
All other things - was the tent fastened or not etc. are just speculations.
Was the tent cut on the other side?
Are the cuts really see through? Where that many tears on the back of the tent that we don't see? Is there a document about this? Source
~ If they allegedly cut the tent to escape there is no reason to cut it on both sides, not to this extend.
Answer:
Case file says "When inspecting the tent, it is established that on its surface there are numerous damages, especially on the right slant of the canopy forming the roof /see scheme №1/." ("При осмотре данной палатки установлено, что на её поверхности имеются многочисленные повреждения , особенно на правом скосе полотна, образующего крышу /см.схему №1/.") The word especially implies that were some cuts on the other side too, just not as many.
Was the tent tampered with?
Is there any mentioning if there was something suspicious about the skis under the tent?
Social media postings hard to link to build theories on the "fact" that the skis under the tent were not positioned properly i.e. were the wrong side up which would testify to the doctoring of the scene.
Answer:
Nothing suspicious. On the contrary - testimonies from 1959 say that all was done quite professionally.
What happened to the tent? Does the tent still exist?
Answer:
Head of Sverdlovsk Forensic Science Laboratory Boris Kretov kept the tent. After Kretov died in the 80s the tent was taken to the garbage container, apparently water pipe burst back in the late 70s and the tent collected mold. The storage policy for evidence as well as case files is that they can be destroyed 25 years after the case is closed. Thank god the prosecutor of the Sverdlovsk region Vladislav Ivanovich Tuykov decided the case files not to be destroyed as “socially significant”, but this did not apply to evidence. Some evidence were taken by relatives and later submitted to Dyatlov Foundation established in 1999, but not the tent. Tuykov is now passed away, lets hope the case files don't have same fate as the tent.
Typical mounting of the tent the Dyatlov group were carrying. Assembled from two old tents stitched together, it was all riddled with holes from the very beginning. The stove used only for warming needed additional rope to be suspended inside the tent. The tarpaulin was burned with many wholes from the sparks that came out from the stove. Grigoriev writes: During the night, holes were added to the tent from the sparks. And in the sun they lit up like stars. The radioman, Nevolin, said "We have become a whole planetarium." None of this is described by Churkina, the expert who examined the tent, because she was asked very specific questions: 1. Is Dyatlov group tent cut? 2. If yes, are the cuts made from inside or outside?
Askinadzi on setting up a tent in winter (from my private mail exchange):
It is at the sole discretion of the leader of the group if to put up a tent on skis or spruce branches. In winter when the days are short, sometimes there’s not enough time to set up a good camp (we arrived at the end point late). This is where you need to show power! Setting up a tent on skis takes much less time than on spruce branches, but there are some nuances - does the group have enough warm clothes to lay for insulation?
If the leader decided, and he had the opportunity, to put up a tent on the spruce branches, it means he had enough daylight for this. But, in this case, he must either be an alpha leader or a the group to work well together. Setting up a tent on spruce branches will take much longer than with skis. At least half of the group will be diverted to this activity. If the hike is multi-day, the leader, even before setting out on the route, decides who will set up the tent(s), so that people know their job (this is practiced in training hikes) and, without a command, take axes and go to harvest spruce branches. Skis were sometimes placed under spruce branches when there was not enough spruce branches.
Ставить палатку на лыжи или на лапник решение только руководителя. Зима, день короткий, иногда мало времени на хорошее устройство лагеря (поздно пришли на конечную точку). Вот здесь и требуется проявить власть! Установить палатку на лыжи нужно гораздо меньше времени, чем на лапник, но есть нюансы - есть ли у группы достаточно тёплых вещей, чтобы подстелить их под себя?
Если руководитель решил, и у него была такая возможность, поставить палатку на лапник, значит, у него было для этого достаточно светлого времени. Но, в этом случае либо должен быть альфа-руководитель, либо хорошо схоженная группа. Установка палатки на лапник займёт гораздо больше времени, чем в случае с лыжами. На это мероприятие будет отвлечено минимум пол группы участников. Если поход многодневный, руководитель, ещё до выхода на маршрут решает, кто будет устанавливать палатку (палатки), чтобы люди знали своё дело (отрабатывается в тренировочных походах) и без команды брали топоры и шли на заготовку лапника. Лыжи под лапник иногда клали, когда лапника было не достаточно.
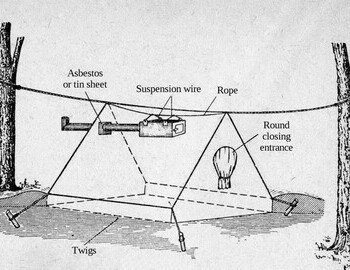
Tent layout
Source 1
A diary entry from January 28 where Lyuda (not signed but it can't be anyone else) saying: "The further section is occupied by me and Zina. Nobody wants to sleep by the stove. We agree that Yurka Kri will sleep there. On the other side sleeps the person on duty (Aleksander Kolevatov). Yurka couldn't stand the heat and after laying down for 1-2 min, he got up and moved to the second section cursing and accusing us of treason." Criminal case. Copy of Dyatlov group diary
Source 2
"The strongest and most experienced Dyatlov and Zolotaryov lie, as always, at the sides, in the coldest and most uncomfortable places. Dyatlov is at the far end of the four-meter tent, Zolotaryov is at the entrance. I think next to Zolotaryov lay Lyuda Dubinina, then Kolya Thibeaux-Brignolle, Rustik Slobodin. I don’t know who was in the center and beyond, but the four guys at the entrance, I think, lay that way." They died with dignity - Interview with M.A. Akselrod
Source 3
"At the far end of the tent were found: bag with maps and documents and Dyatlov camera, tin box with money, Kolmogorova diary. Next lay Dyatlov and Kolevatov jackets." Case file 34
Source 4
"Dyatlov belongings were discovered at the very end of the tent (a field bag containing money, documents, diaries, a camera, etc. After that lay Slobodin and Kolevatov I think, because there were found their belongings." Case file 315
Source 5
Yuri Yarovoy "The highest category of difficulty"
The expert (Churkina or Mihaylova according to Почемучка) was interested in the curtain - this is what we called the sheet at the entrance of the tent. "Why is it there? It's in the way when entering…" Yuri Yudin: I explained to her that we had two departments: the far one was for men, and at the entrance it was for girls...
----------------
Эксперта интересовал полог — это мы так называли простыню у входа палатки. «Зачем она? Она ведь мешает входить…»
Я ей объяснил, что у нас было два отделения: дальнее — мужское, а у входа — для девушек…
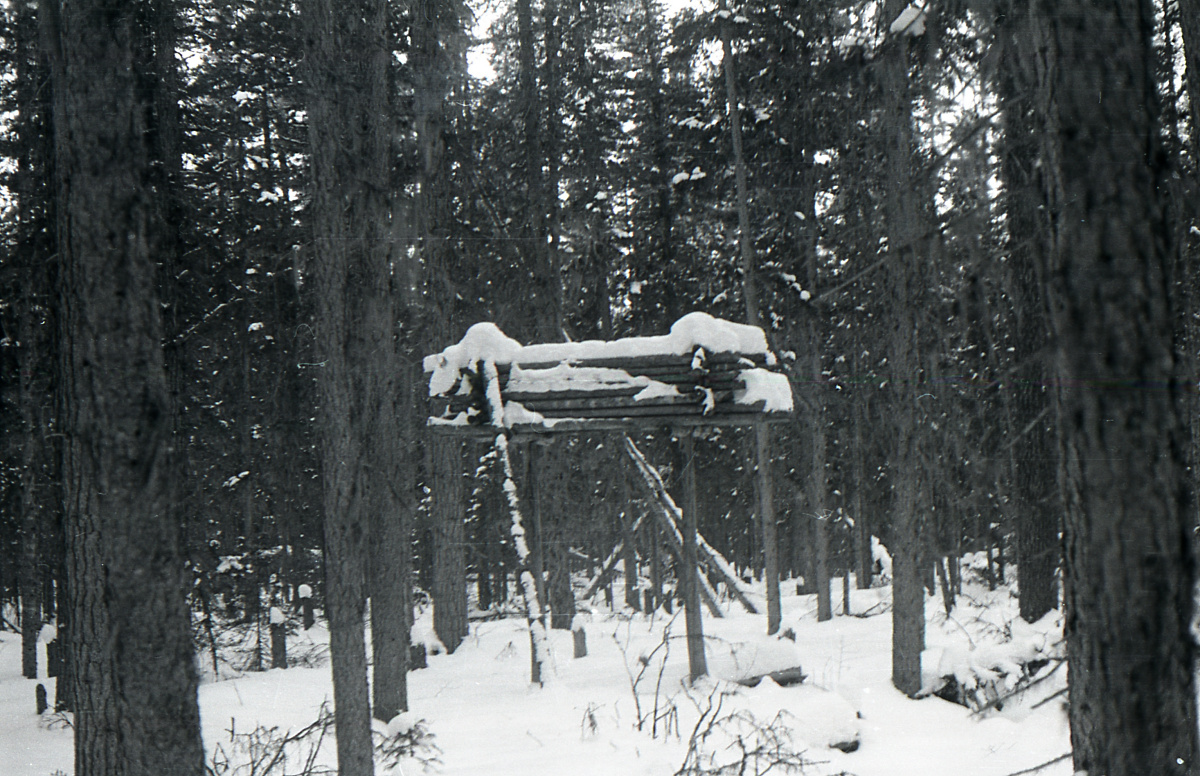
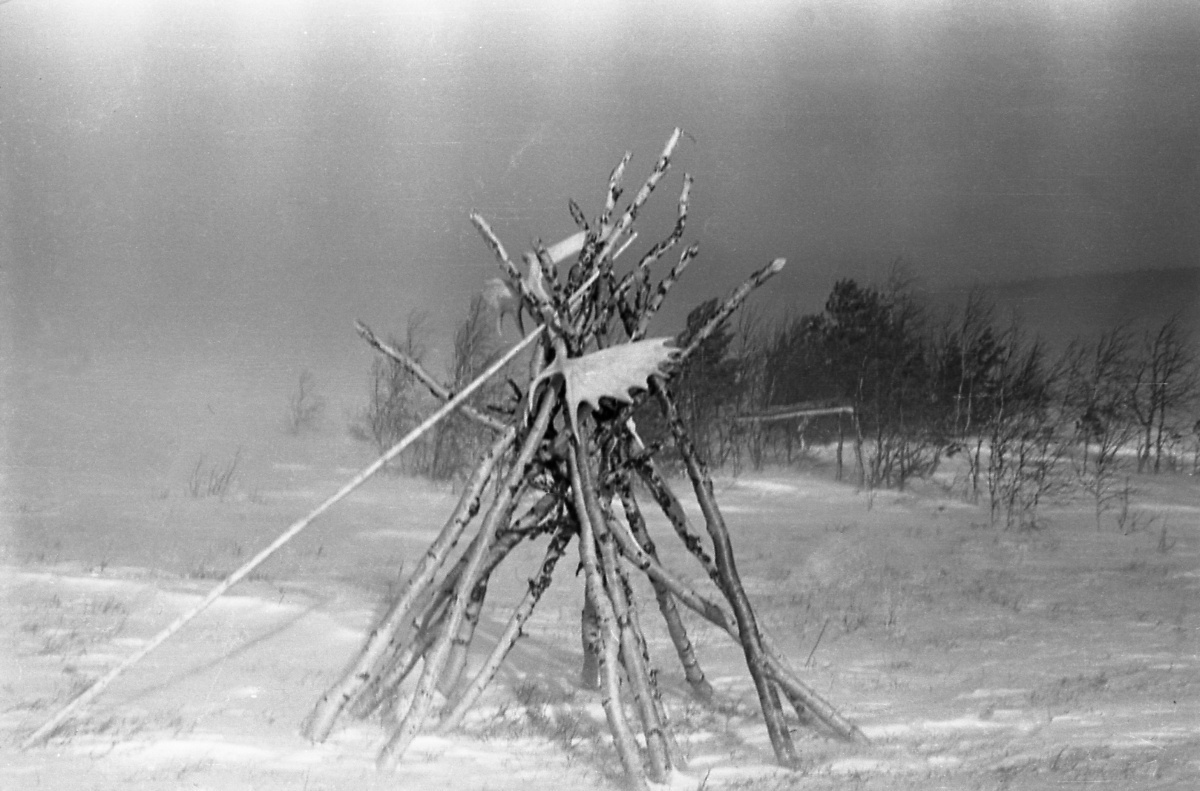
Labaz
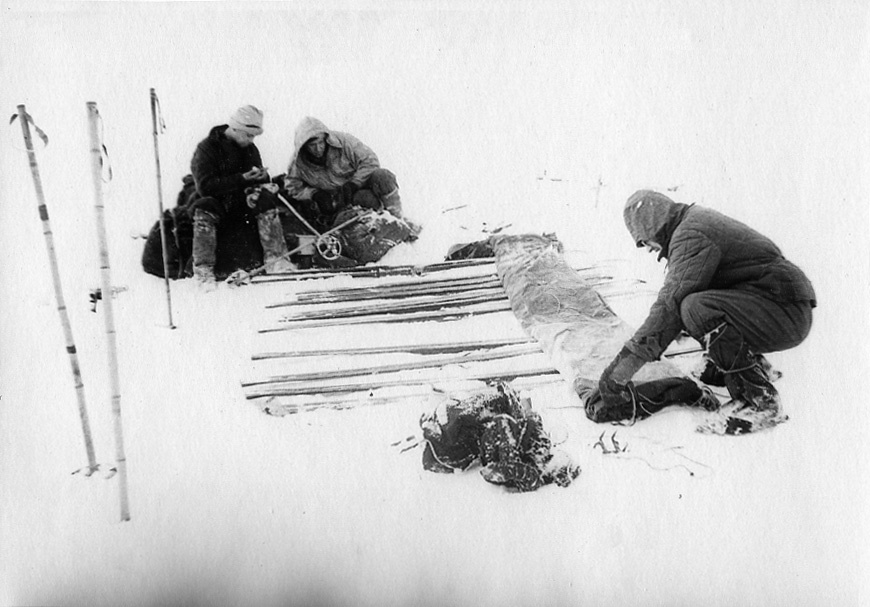
The storage site where Dyatlov group left provisions for their way back and lighten their backpacks for the ascend. In different sources they call the site "labaz". Mansi rise platforms to store their game to pick it up later. Dyatlov group labaz seems to be constructed in haste – in a snow pit, rather than in trees beyond the reach of animals, as it was more common. In last entry of the group diary on January 31 Dyatlov wrote "I can't even start thinking of setting up a labaz". That can explain why the labaz was in this pitiful state. One item in particular raises questions: Dyatlov’s boots. Why continue on ski without his boots? Yudin’s answer was that, with this particular straps over the ski boots it was possible to ski in valenki and, moreover, Krivonischenko, for one, preferred to ski in his felt boots as well. Then, presuming they will be on their skis the whole time an extra ski boots will make uncomfortable extra weight. Their cache was found marked with one ski propped in the snow and a gaiter slipped onto it. See Protocol inspection of the storage (labaz).
Skis
In the University equipment inventory there is mentioning of one spare pair of skis. Yudin returned on his skis. Ski professionals say that extra pairs of skis are essential for such a long route. Traditionally, the last person in the line drags them behind with a rope. In this photo we see Krivonischenko carrying skis on his back. It was probably this extra pair that was used to make Kolevatov's sled mentioned in their satirical propaganda leaflet Evening Otorten, see the Technical News section. In the case files we have 3 different counts of the skis found at the tent and the labaz:
- Feb 28, 1959 The protocol of the hikers camp site mentions 8 pair of skis on the bottom of the tent, no mentioning of spare pair of skis. Signed by Tempalov.
- Apr 15, 1959 Slobtsov who found the tent and the labaz, says "around the tent in the snow stood ski poles and spare skis - 1 pair" (sheet 298 back) and "a pair of spare skis" in the labaz (sheet 300).
- Apr 18, 1959 Tempalov in his testimony says 9 pair of skis, all of them under the bottom of the tent and additional spare pair of skis in the tent.
My conclusion is that there were total of 9 pair of skis at the tent, 8 under the bottom of the tent, and one pair propped in the snow, but it was not a spare pair, just the ninth pair.
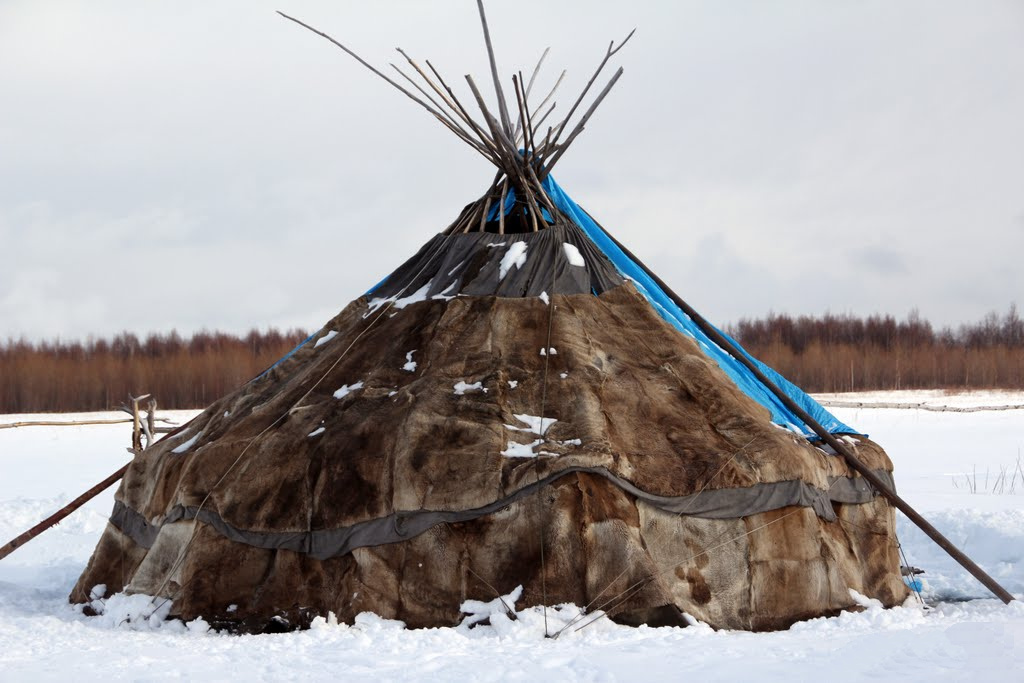
Mansi chum
A Mansi chum (definition) was observed North-East from where Dyatlov group pitched their tent on the night of January 30. A trail leading to the chum was passing 200 feet from where they camped.

This construction is referred to as chum and was found 1 km from the tent (according to Cheglakov's testimony).
Theory 1
The defenders of the Mansi theory say that the hikers may have been killed because they enter Mansi hunting grounds. Here follows an excerpt from Svetlana Oss "Don't Go There":
‘He (GOD) would be brought a sacrificial rooster. And when there wasn’t a rooster, it was said, it was necessary to steal a sacrifice, a Russian baby.’ Roma looked at us expectantly. ‘Well that was a long time ago, and now they don’t do that. Barbarism. A rooster is better.’
In the criminal case, the latter part of the statement of Ivan Uvarov, the old man who said the wind could produce some terrible sounds, says:
About the Mansi, I know that their sacred mountain is about forty km south from the place of the deaths. Forty-five years ago there was one accident with a hunter from the Pershino settlement. He climbed that mountain and took part of the food they had left there for their gods. He brought some of it back to his home. He did this again but then disappeared and was never seen again. There were some rumors he took an arrow designed for hunting animals."
Theory 2
That same Vladimir Androsov who Svetlana Oss is quoting commented in an interview on this particular photo of the chum:
The group had one ice axe yet two were found
Ice axe 1
An ice axe was found outside the tent close to the entrance.
Ice axe 2
In the criminal case file there is a list dated March 3 "Things brought from the Labaz" where there is an ice axe. It is not clear whether this ice axe was the same one found by the tent or if there was another one in the labaz. No ice axe was initially reported by those who found the labaz. Or, if there was indeed an ice axe in the labaz this means the ice axe found by the tent does not belong to the group.
Why the livor mortis spots did not match the position of some bodies?
Theory 1
On Doroshenko, Kolmogorova and Slobodin the livor mortis spots were on the top surface of the body. This allows speculations that the bodies were moved after their death.
Theory 2
In his book Rakitin speculates that the medical examiner Vozrozhdenniy mistook frostbite erythema for livor mortis. Article is citing the forensic bible at the time "Forensic medicine" 1953 by M. I. Rayski where there is no mentioning of frostbite erythema but on p. 233 it says that livor mortis in frozen cadavers change color when carried in a warm room from purple to light red, and then darken again. Same thing happens with frostbite erythema when defrosting a corpse. So the author says "it is not surprising that the medical examiner Vozrozhdenniy thought that he sees livor mortis spots".
Maps with the ravine and den where Dubinina, Kolevatov, Thibeaux-Brignolle and Zolotaryov were found
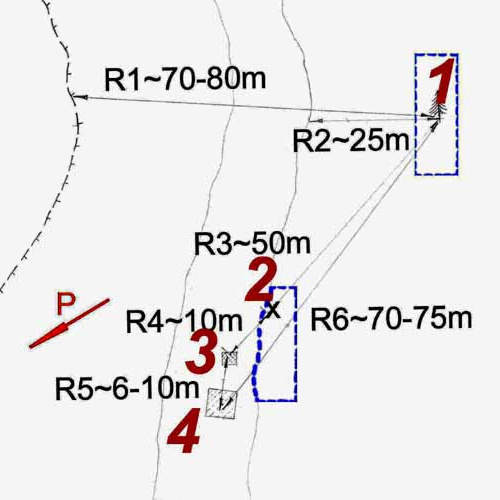
Map by Aleksey Rakitin - authour of the book "Dyatlov Pass"
1 - cedar, 2 - cut pants and sweaters, 3 - bodies 4 - the den. "P" the direction to the tent. Distances: R1 - the distance from the cedar to the edge of the forest, R2 - the shortest distance from the cedar to the ravine, R3 - the distance from the cedar to the cut pants and sweater, R4 - the distance from the cut pants and sweater to where the bodies were found, R5 - the distance between the bodies and the den, R6 - the distance from the den to the cedar. The blue dashed lines show the area where the fir trees where crushed to carry branches for the flooring of the den.
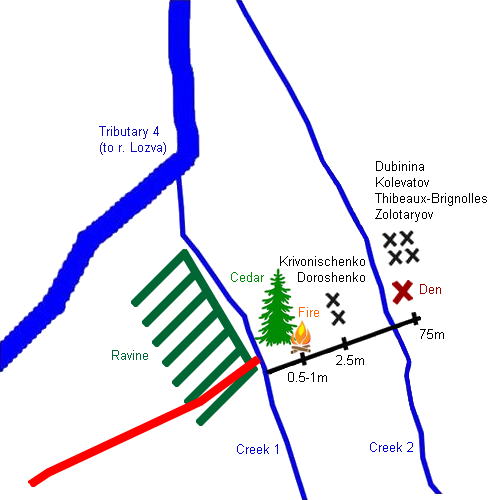
Map by Mihail Sharavin - member of the search party that found the first bodies of Doroshenko and Krivonishenko, 2m from the cedar, the tree being between the tent and the bodies. When the bodies of Dubinina, Kolevatov, Thibeaux-Brignolle and Zolotaryov were found Sharavin made a note of what he thought is the location of the bodies, a reconstruction made by NAVIG in 2009 shows den and bodies north-west from the tree and not south-east as shown in Rakitin's map.
Why are these maps so important? The slope of the ravine has a 5-7 m drop to a rock bottom of creek 1 (on Sharavin's map) which could have let to a dangerous fall in the dark and caused the traumas.
More maps of the ravine
Passports on Dyatlov Pass
Fact is that on the hikers only two passports were found, Dyatlov's in his field bag that remained in the tent (case file 6) and Slobodin's in his breast shirt pocket (case file 96)
Kolmogorova had an dormitory pass with a photo among the belongings that were fetched from the tent. Where was it originally is not clear, all the small items were bagged into random backpack and airlifted to Ivdel where journalist Grigoriev made the first inventory and identify the belongings with the help of Yudin. (case file 12)
From "1079" book: "When delivered to Ivdel, the bodies were transported from the airport to the N 240 Central hospital serving the administration staff of N 240 and placed in the morgue. The driver of the truck was Stolyarov, the driver of the Northern Expedition, who had been detailed to the Ivdel airport sometime before the beginning of the search for the missing hikers.
By around 2:00 PM Pletnev and Vishnevskiy had completed their list of items brought from the cache site. In the morning, with the help of Grigoriev, they had already completed their inventory of the group’s belongings, which were brought to Ivdel on
The big deal is that if they needed their passports and they brought their passports, then where are they?
I started my inquiry about the passports after the interview with writer and Dyatlov case researcher Oleg Arknipov. He remembered that Natalya Varsegova, the Komsomolskaya Pravda journalist who initiated the exhumation of Semyon Zolotaryov wrote in the Russian forum taina.li: "Semyon's passport was returned and destroyed back in 1959. The registry office does not keep the passports of the deceased." This is all we know. Who returned it? Sogrin, who Semyon Zolotaryov stayed with before going on the expedition does not remember any passport. Zolotaryov's funeral was delayed so his mother could attend. Zolotaryov didn't live with his mother and he needed his passport for work and travel, so she couldn't have brought it at the funeral. Natalya Varsegova: "The registry showed the signatures of Semyon’s mother. This means that she handed over the passport. The conclusion is that the passports were given to relatives, and they handed them over to make inquiries and receive the death certificate." So Zolotaryov’s passport was found and returned to his mother but in the case files there is no mention of his passport. Where was Zolotaryov's passport, who found it and when?
Did the hikers need their passports on the trek?
Controversial, but it seems like they carried their passports, especially when going though sensitive areas e.g. close to the border or forced labor camp zones.
Recollections of contemporaries hikers
Zinovyov: "Having passed the necessary controls and checks of the route books and passports of the participants in the administration of the Vizhay settlement, the groups of Yuri Blinov and Igor Dyatlov hurried to their routes." Read more →
Gudkov: "Of course, we had passports with us..." Read more →
Askinadzi: "You definitely needed a passport on a hike, at least for the leader." Read more →
Money on Dyatlov group
From Rimma Kolevatova's testimony Case file 270:
"The funds allocated for the organization of such hiking expeditions are very scarce. This was a 22-day ski trip to remote areas in winter conditions. Naturally, it is supposed to have a supply of nutritional products, in particular, each hiker needed to have an inviolable supply of chocolate (just as they had a box of matches each in the breast inside pocket of the suit). The institute allocated to each student only 100 (one hundred) rubles as an aid, which, of course, was not enough. The remaining funds were collected by the group members themselves, amounting to 350 rubles."
* * * * * * *
From Dyatlov's plan for the expedition Case file 207:
| Cost estimate |
|
1300 rubles for 9 people
Received 1000 1100 rubles from the trade union committee
We have 1100 rubles for the expedition
* * * * * * *
| found | returned | missing | ||
| Dyatlov | 975 | 700+271 | Ivanov is not sure where Case files vol.2-42 Case files vol.2-40 UPI 700, Dyatlov's father 271 Case files vol.2-46 In 1961 the amount of 700 rubles were given to Dyatlov's father Case files vol.2-51 |
|
| Kolmogorova | 5x1 | 5(+1) | In the pockets of her jacket found in the tent Case file 12 Case files vol.2-42 Receipt Case files vol.2-9 |
|
| Dubinina | 35 | 35 | In the pockets of her ski trousers found in the tent Case file 14 Case files vol.2-42 Receipt from Dubinina's mother Case files vol.2-71 |
|
| Doroshenko | 10x2 | In the pockets of his jacket found in the tent Case files 15 In the pocket of his storm jacket Case files vol.2-41 |
||
| Thibeaux | 3+5(+1) | 8 | At the cedar Atmanaki's testimony Case file 216 "Around the campfire are discovered charred sock and a checkered shirt. In the shirt money - 8 rubles." Case file 3 In the pocket of his shirt Case files vol.2-42 |
|
| Slobodin | 310 100+50x4+10 |
310 | On the body in the breast pocket of his checkered shirt Case file 15 Receipt from Slobodin't father Case files vol.2-8 |
|
| Yudin | 250 | Receipt Case files vol.2-62 | ||
| Bienko | 350 | Receipt Case files vol.2-61 | ||
| Krivonischenko | ? | |||
| Kolevatov | 3x100 | Rimma Kolevatova says she gave her brother 3x100 rubles, they are not found Case files vol.2-50 | ||
| Zolotaryov | ? | |||
| 700 | In a tin can Case files vol.2-42 In a tin can with 10 rolls of films Case file 6 Income cash order Case files vol.2-63 |
|||
| 2053 | 1930 |
* * * * * * *
By origin the money on the Dyatlov group were:
1100 from the committee, looks like they remained in Dyatlov
3850 (350 each) to enroll in the expedition, should be in Lyuda
Personal money in their pockets, some of them are missing, but there is no logic unless only some bodies were tampered with
Expenses that we know of:
- Lyuda spent 200 for a fabric that is used for summer clothes and she curses herself to have done this foolish purchase only because she had the money for the expedition. Surely she intended to return the money when they got back.
- Nine tickets for the train (not ten), Lyuda hid under the seats. Feeling guilty?
According to Dyatlov's calculation above this amounts to 585 rubles (nine tickets of 65 rubles in one direction) - Food, according to Dyatlov 16 rubles per person per day for 20 days = 3200 rubles
- The 700 found in the tin can with films, I believe those were set aside to be returned to Bienko and Yudin.
According to my calculations Lyuda had 3850-200=3650
I believe Lyuda bought the tickets or else Dyatlov would have insisted on buying the correct amount, he won't take the risk.
Tickets: 3650-585=3065
Food: 3065-3200=-135
The food was not bought all at once. I believe this is what made Lyuda postpone when she would admit to Dyatlov the shortage of 200 rubles. I believe that maybe she thought that she could cover it for longer, it was not a lot of money after all but Dyatlov kept the public money on him. So she had to tell him. Then my speculation is that he decided to put aside the money (the 700 in the tin can) they had to give back to Yudin and Bienko.
Was this the cause for Lyuda's bad mood? That the money was running out, maybe she hadn't told Igor about the 200 rubles spent on cambric aka batiste?
This has nothing to do with the tragedy, only explaining Lyuda's sulking which has always intrigued me. Why was she in such a bad mood?
This is not the most important observation about the money in the Dyatlov group though. I will point to something that is characteristic in many aspects of this investigation. The fact that things do not add up.
Money is left at the scene i.e. robbery is not the motive. But how come Krivonischenko, Kolevatov and Zolotaryov have no money on them, none whatsoever? Unless they were misplaced prior to the official discovery of the tent and bodies. For example when they were brought to the Ivdel morgue, undressed, examined, and then returned back to be officially found again. Read more details of this theory from book "1079".
We do not have Lyuda's notes of the expenses, what was bought, when, how much did it cost etc. This is also explained by the theory that someone else made the labaz where the supplies were found because the original labaz was taken apart not expecting the massive search operation. When the searchers read the diaries and started looking for a "labaz" this is when the one we know of was found, with products like sausages, sugar and cocoa not touched by the animals for a whole month. Dyatlov's original list of food supplies and the notes how much everything cost when they bought it, all this is missing. The case files contain what was found, not what the group carried with them. More troubling is that the rest of the papers are found in Dyatlov's field bag, but nothing about food supplies.
Lyuda's diary is not included in the case files and not all the pages were scanned. It is not known where the original diary is.
* * * * * * *
From Lyuda Dubinina's diary:
23 january. It’s the last day of preparations and everything has been quite hectic. From eleven in the morning I was scampering between stores buying different bits and pieces. I foolishly bought five meters of cambric that cost all the mon cost 200 rubles.
I discussed with Vladimir Askinadzi what could have been the fate of these "five meters of cambric". Here is what he said:
The word "foolishly" itself says a lot! The purchase was not planned or listed. Lyudmila simply "ran into" another "deficit" and, like any woman of that time, could not resist. She probably had to stand in line for a while.
I think the money was public, otherwise she would not have remembered about the purchase.
Dyatlov could forgive this "initiative" since Gordo did give him some money (this is my personal assumption!).
Lyuda could have kept it at home only with Dyatlov's consent, since it was bought with public money. At that time, public property was treated very honestly. Most likely, she left it at home, and would have paid the money (with Igor's knowledge) after the hike. We used to do that. All things bought along the route (books, some things, etc.) were bought (with my permission) sometimes with public money, taking into account that at home they would be returned to the common fund, since after the hike money is always needed to pay for unforeseen expenses for preparing reports, stands, etc.
А само слово «Сдуру» говорит о многом! Никакими планами и списками покупка не была предусмотрена. Людмила просто «налетела» нечаянно на очередной «дефицит» и, как любая женщина того времени, не смогла удержаться. Наверняка пришлось ещё постоять в очереди.
Думаю, что деньги были общественными, иначе бы она о покупке и не вспоминала.
Дятлов мог простить эту «инициативу», поскольку Гордо всё же дал ему немного денег (это моё личное предположение!).
Люда могла его оставить дома у себя только с согласия Дятлова, поскольку он куплен на общественные деньги. В то время к общественной собственности относились очень честно. Скорей всего она оставила его дома, а деньги (по договорённости с Игорем) внесла бы после похода. Мы в своё время так делали. Все вещи, купленные по маршруту (книги, какие-то вещи и т.д.), покупались (с моего разрешения) иногда на общественные деньги с учётом, что дома они будут возвращены в общую копилку, поскольку после похода деньги всегда нужны для оплаты непредвиденных расходов по оформлению отчётов, стендов и пр.
* * * * * * *
Valentin Yakimenko is describing a similar incident: "Once on a trek, one participant, tempted by the thought of the condensed milk in his backpack, secretly from the group ate one can. Regretting afterwards, he told Igor about this. Igor did not scold or shame him. He kept silent. And then he said: "When we return to Sverdlovsk, you will pay the cost of the condensed milk to the group’s cash desk." This case was remembered for many years..." From Ural Stalker 2009 №1
* * * * * * *
You can discuss this topic on Dyatlov Pass Forum.
Knives
DYATLOV
Case file 13 - a penknife with stringed carabiner (in the pockets of the tarpaulin jacket and trousers, IN THE TENT)
THIBEAUX-BRIGNOLLE
Case file 14 - a penknife and a Finnish knife (in the pockets of the windbreaker and trousers, IN THE TENT) Since he didn't have a permit the knife was not returned to the family.
SLOBODIN
Case file 15 - penknife (in a pocket of his ski trousers, on his body)
Case file 310 - A "big knife" presumed Kolevatov's, is mentioned by Tempalov who was the first investigator at the scene. He cut the tent to get access inside.
Lev Ivanov initially didn't want to return the knife to Kolevatov's relatives but then had change of heart and offered Rimma Kolevatova to choose either the knife or the sheath. She chose the knife. Now isn't this weird. Here is the receipt that has spawn the legend that Kolevatov had a permit for his Finish knife.
May 6, 1959
Case file 341 "Ebonite sheath and a tablespoon of white metal were found under the snow at the location where the Dyatlov group tent was found." NEAR THE TENT
Where did the knife that cut the branches go?
Theory 1
In the Resolution to close the case Lev Ivanov says that Krivonischenko’s knife was used to cut the trees since it was found in the ravine next to the last four bodies. The Protocol of inspection of the scene where the bodies were found goes into great detail about everything found there, including number and kinds of trees as well as clothing but never mentions any knives.
Theory 2
From Captain Chernyshev’s testimony: "It can be assumed that at the fire besides Doroshenko and Krivonischenko there were other people since... No knifes were found on the bodies but the branches for the campfire were cut with a knife."
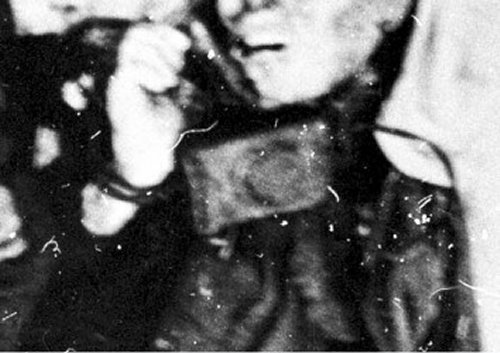
Whose burnt jacket is Slobodin posing in?
On this photo Slobodin is posing in a burnt quilted jacket. We know it is not his because Zina writes in her diary: "Burned mittens 2 and Yurkin's quilted jacket."
Theory 1
When is writing in her diary Zina is usually referring to Yuri Krivonischenko as Yurka Kri (or Kriv.), and Yurka only is Doroshenko.
Theory 2
Protocols of item identification (Case files 233)
Krivonischenko, after examining the presented items, said that his brother, Georgiy Krivonischenko, owned the following items:...
8. Padded jacket blue, burned...
All of the above items Igor Aleks. Krivonischenko identified with certainty.
Protocols of item identification (Case files 240)
V. N. Kostrulin, after examining the equipment, stated that the following items belonged to his friend Y. N. Doroshenko:
1. Padded jacket blue...
V. N. Kostrulin identified with certainty all the items listed above.
Notorious frame №34
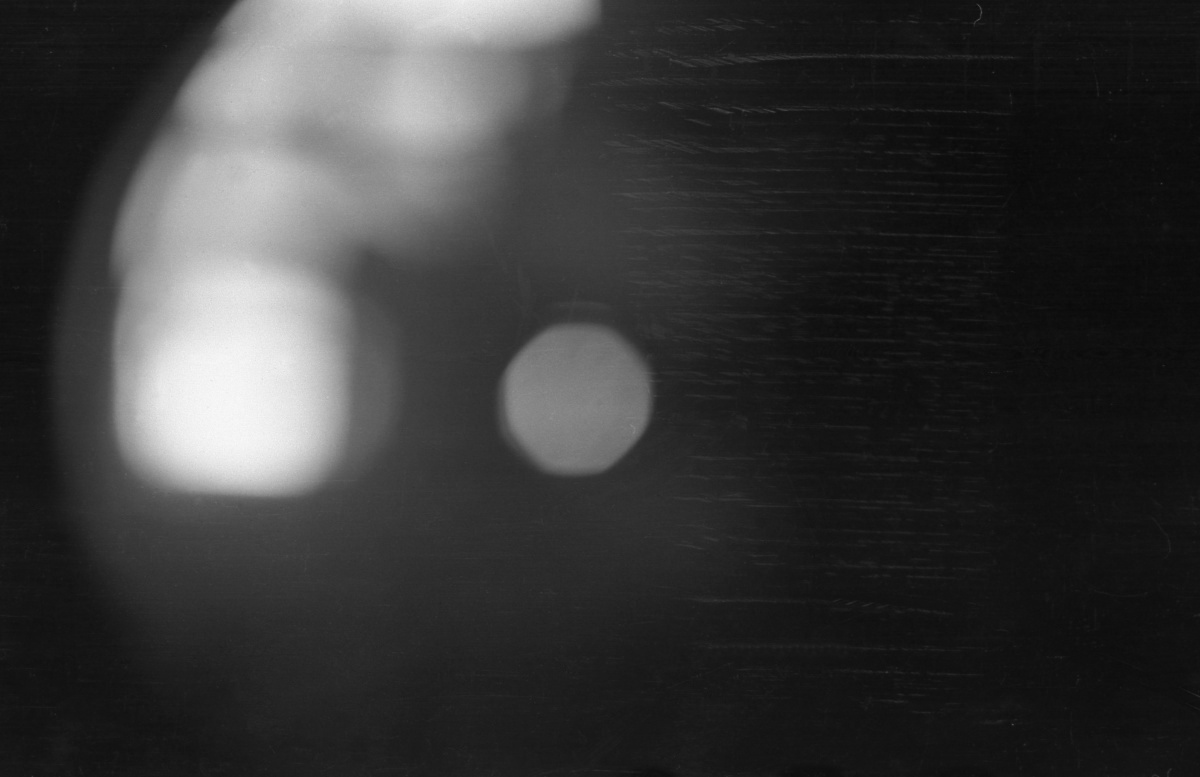

This photo is often referred as №33 depending if you count frame №15 which was discarded till recently (or at least until Zolotaryov's film suddenly start showing so much potential) as poor quality.
Theory 1
UFOs, massive alien invasion, alien sacrifice, face peering into the tent, fireballs, engine of a falling missile etc.
Theory 2
The technician in the crime lab was given a camera with a film inside which he has to develop and give back to the investigators. Old cameras have film in a cartridge, the camera makes a photo by (1) pressing the shutter and then (2) using the film advance lever to draw next blank frame from the cartridge. Some people do (2) right after (1), some do (2) right before the the shot. The technician has no way of knowing if the camera is in position (1) or (2). Rewinding the film is only possible in position (1). The technician can either use the film advance lever which will not work if the camera is in position (2) or press the shutter which will not work if the camera is in position (1). Pushing the lever too hard can damage the film. Usually the lab technicians pressed the shutter and if doesn't go off then the film can be rewinded. If it does go off then the film can also be rewinded but the there is one last technological photo which captures whatever is in front at that particular moment - wall, ashtray, table, papers, and a lot of unidentifiable objects nearly always out of focus. The shutter of Krivonischenko's camera was cocked, so the notorious photo №34 came to life. Initially this frame was not presented in the investigation as pаrt of the film, and it should have remained that way, because introducing it at a later time inflated even further the monstrous significance that this photo is gaining.
Radioactive contamination on hikers clothes


Two sweaters and pants
The original report for all findings for radioactive testing are published here - Radiation Analysis Report
Abnormally high readings show:
- brown sweater on Dubinina - 9900 decays/min 150 cm2
- trousers lower part on Kolevatov - 5000 decays/min 150 cm2
- the waistband of sweater on Kolevatov - 5600 decays/min 150 cm2
Vladimir Levashov, the main radiologist of Sverdlovsk, conducted the examination. Upon rinsing the clothes, it was shown that contamination could be decreased by between thirty and sixty percent. The rinse was conducted in a standard test using cold running water for three hours.
Could the clothes be contaminated above the normal level by normal circumstances without having been in the presence of a radioactive-contaminated place?
No
Were the samples examined by you contaminated?
As mentioned in the conclusion, there is contamination by a radioactive substance or substances. Beta emitters were found on certain separately-sampled areas from the samples I received. For example, the sample from Dubinina (brown sweater), at the moment of examination, had a decay rate of 9900 beta particles per minute for 150 cm2. After rinsing, it displayed 5200 decays of beta particles per minute from 150 cm2.
Normally, contamination of beta particles from 150 cm2 should not exceed 5000 before rinsing. After rinsing it would be expected to find a normal level equivalent to the natural base level, which is provided by natural cosmic radiation for all people in a particular place. This is the normal rule for those who work with radioactive materials. From Kolevatov, the sweater yielded a display of 5600 particles per minute before rinsing, falling to 2700 particles per minute after rinsing. In your data it’s indicated that, before they were sent to us, all of these objects had been in running water for quite some time, which means they had already been rinsed.
Note: In the original document Levashov refers to Dubinina and Kolevatov as body №4 and body №1.
Can we conclude that the clothes were contaminated by radioactive dust?
Yes. Contaminated by radioactive dust which fell down from the atmosphere, or these clothes were contaminated while working with radioactive substances, or via contact. This particular contamination exceeds the normal level for people who work with radioactive substances.
What was the real degree of contamination of some objects considering that they were in running water for about 15 days?
One can guess the contamination of some parts of the clothes was many times more. But we must also consider that the clothes could have been washed with differing degrees of intensity.
"Now we know snowmen exist"
Theory 1
In Discovery "Russian Yeti: The killer lives" Libecki quotes a cryptic passage written in a newspaper the students brought with them "From now on we know that the snowmen exist".
Numerous sites plain misquote Evening Otorten paragraph. Here is an example: "From now on we know the Snowmen exist. They can be found in the Northern Urals, next to Mount Otorten".
Theory 2
The only written piece where snowman (or Yeti) is mentioned is in Evening Otorten №1, the satirical propaganda leaflet Dyatlov Group put together at the night of the incident. The case file does not contain a photo of this flyer, only a transcript of its content. You might think that researchers would want to consult the original document in order to independently authenticate such an apparently important clue, but they do not.


What happened to the original paper Evening Otorten?
Nobody knows. The original is not in the criminal case. Moreover, none of the searchers saw it in the tent. Maslennikov did not see the leaflet in the tent himself. Someone radiograms from Ivdel to Maslennikov (who is on the pass leading the search operation): a propaganda leaflet was found in the group’s belongings. (underlined with red on the page from Maslennikov notebook 2) This radiogram is also not in the case files.
Where there burned trees in the area?
Lev Ivanov is the lead investigator. For the first time we hear about this from his article "The Mystery Of The Fireballs" L. Ivanov, "Leninskiy Put" newspaper, Kustanay, November 22 and 24, 1990 "When, in May, I and E. P. Maslennikov* examined the scene of the incident, we found that some young trees on the forest tree line have traces of burning, but they are not in concentric shape or any other system. There was no epicenter. This once again confirmed a source of heat ray or completely unknown to us energy acting selectively - the snow was not melted, the trees were not damaged. It seemed like when the hikers walked on their feet more than five hundred meters down from the mountain, someone dealt with some of them as direct targets."
* Maslennikov didn't go to the pass in May
Was there "skin found on the bark of the cedar"?
The only place this is mentioned is Ivanov's "The Mystery Of The Fireballs" which was published 30 years after the incident to get attention back to the cold case which he didn't solve in 1959:
"On the bark of the tree there were frozen (it’s scary to even say it!) their skin of their inner thighs and scraps of underwear."
Time of death
- There is a radiogram from March 1st send by Maslennikov stating that the date of death is established
The date of the disaster is exactly established to have occurred on the night of February 2nd. See the telegram → - On March 1st all the bodies are still on the pass. They will be lifted off on March 3rd.
- On March 1st the tent and all belongings are still on the pass, they will also be lifted off on March 3rd.
- The propaganda leaflet (dated February 1st) will be found among the items from the tent only on March 4th, which coincides with the fact that on the 3rd the items are lifted off, and on the 4th they are taken apart and protocoled.
- There are no entries in any of the known diaries after January 31st
Question: On the basis of what, by March 1st, Maslennikov precisely established that disaster occurred on the night of February 2nd?
Answer: My personal opinion is that although not stated anywhere, Maslennikov must have read Evening Otorten, maybe looked into a diary or two and acknowledged that there are no entries after 31 Jan, and stated in the radiogram on 1 Mar that they have concluded that the deaths have occurred on the night of February 2nd.
Question: Another aspect is what the night of February 2nd means - is it the early hours i.e. the night 1-2 Feb or the night 2-3 Feb?
Answer: In Russian and most European countries the following is used:
- from midnight to 6AM - night
- from 6AM to noon - morning
- from noon to 6PM - afternoon
- from 6PM to midnight - evening
How many cameras did Yudin say there were
more than 4
Aleksei Rakitin in his book "Dyatlov Pass" says:
Yuri Yudin (the only surviving member who felt sick and turned back on January 28 from North-2) kept saying that the cameras were more than 4, nearly everybody in the group had camera. The investigation didn't seem to care.
only 4
The following is copied throughout the net in the context of the camera found on Semyon Zolotaryov:
We should add that this camera became a complete surprise to Yuri Yudin. He assumed the group had only four cameras that were found in the tent. And all of a sudden a fifth camera turned out on the body.
Who did Yudin give his vest that was found on Dyatlov
Kolevatov
From the "Protocol inspection of items found at the scene" (Case files sheet 13):
One piece of clothing found on I. A. Dyatlov body described in the autopsy report was a fur vest trimmed with blue satin. Yuri Yudin said that the vest belonged to him, and on 28-Jan-1959 he gave it to S. Kolevatov.
Doroshenko
Yuri Yudin himself said the following in a letter dated May 14, 2008:
As for the inconsistency in the inventory, he has a quilted jacket, then perhaps this is an incorrect entry by investigator Ivanov. He wrote the inventory as he needed in his own handwriting. He wrote that I gave my fur sleeveless jacket to S. Kolevatov, while I gave it at the 2nd Northern to Y. Doroshenko.
He attributed to me that I allegedly identified the intimate parts of Zina's clothing and what the first five bodies were found in, but naturally I could not do this since I was not present at the autopsy and undressing of the bodies... I was naive and signed the inventory without reading it, firmly believing in the actions of the investigator.
But this is not quite it.
Doroshenko had borrowed the same type vest from a friend before the trek. This is a line from the protocol of identification of the items by relatives:
Case file 240 (back)
3. Sleeveless fur vest borrowed from Farid Gaynutdinov, course R-463
In the protocol of the items found in the tent Yudin said that the following items belonged to Kolevatov. Note that they were not found on Kolevatov, so Yudin could have been easily mistaken. This could be Doroshenko's vest, and he could have unwillingly contributed to the mess in the case files. Ivanov is not solely to blame.
Case files 16
8. Identified as Kolevatov's belongings: black backpack.
Blanket of soldier cloth, jackets and pants, fur vest...
On the other hand Kolevatov's relatives did not identify any such vest, so it must belong to someone else.
Was Semyon wearing Lyuda's clothes?
May 4, 1959, 75 meters from the campfire, in the direction of the valley of the fourth tributary of Lozva, i.e. perpendicular to the way of the hikers from the tent, under a layer of snow 4-4.5 meters, the bodies of Dubinina, Zolotaryov, Thibeaux-Brignolle and Kolevatov were found. On the bodies, as well as a few meters from them, Krivonischenko and Doroshenko's clothes were found - trousers, sweaters. All clothing has traces of smooth cuts, as already photographed with the bodies of Doroshenko and Krivonischenko.
The dead Thibeaux Brignolle and Zolotaryov were found well-dressed, worse dressed Dubinina - her jacket made of artificial fur and a cap were found on Zolotaryov*, Dubinina's naked leg was wrapped in Krivonischenko's woolen pants.*
Was Semyon wearing Lyuda's clothes?
According to the autopsy report, Zolotaryov is wearing a “brown sport button-down jacket with a button”. And a "tarpaulin green fur jacket on sheepskin" is found on Tibo, which, according to the description, resembles Luda's jacket, which was not found in March.
As for the cap, which also "turned out to be on Zolotaryov", in volume 2 there is a note written by Ivanov himself, that "the green cap is on Tibo".

As for "Dubinina’s bare leg wrapped in Krivonishchenko’s woolen trousers"
According to the autopsy report: Left leg - part of lower leg and foot wrapped in a gray woolen burnt flap from a jacket with a sleeve
Protocol of inspection of the scene where the bodies were found: «half of the sweater is wrapped around the right leg - a beige color sweater»
Resolution for radiological testing: brown sweater from № 4 (№4 – Lyudmila Dubinina, according to the autopsy protocol number, coincidence in the number of decays - 9900)
Thus, the statement about the “woolen trousers” is not confirmed by any document and even contradicts the resolution on conducting the Resolution for radiological testing, written by Ivanov himself.
Where some cameras/films taken from the tent by members of the search party?
The question about the film development is very complex.
I haven’t read anywhere that someone from the search party found and took a camera/film and developed the film without permission.
It is known (from memoirs) that several students did print photos from the group’s cameras back in Sverdlovsk at the request (or assignment) of the prosecutor’s office. This is Bienko, and besides him - students of UPI Chubarev, Bychkov, Yudin, Sogrin, Shulyatiev, Stadnikov, Brusnitsyn, and Plastun.
Vladislav Bienko is UPI student, Zolotaryov took his place in Dyatlov group. In UPI there were rumors circulating that he was not allowed to do the trek due to skipped exams. The Komsomol sent Bienko to a logging camp instead. Lev Ivanov trusted Bienko to develop some of the films found in the tent - this is the official version.
There are too many students who printed photos. It is possible that not all memories can be trusted. There are no documents of 1959 about this, only modern recollections.
Zolotaryov's camera
Zolotaryov and Thibeaux were better clothed and wearing some kind of footwear (felt inner shoes). This and the fact there were traces close to the tent from urination funds the speculation that the two went out to relief themselves. It is natural to put some clothes on, although not fully clothed for a hike in the night. Zolotaryov took another camera, not the one found in the tent. Something raised his interest to take the camera with himself, and then run with it down the slope, into the den. Whatever/whoever chased the rest of the group out of the tent must not have seen Zolotaryov and Thibeaux or else they would have made them take of their extra clothes and especially the camera, since Zolotaryov could have capture a compromising shot. There are two people's footsteps joining the barefooted group a little further down the slope. The perpetrators might have not seen the two till then at all.

The body of Semyon Zolotaryov, shorly after being found, with what appears to be the camera or camera case, affected by water, around his neck. The camera stayed on Zolotaryov's body under the water for 3 months. To me it is even more incomprehensible why did the attackers left the camera on Zolotaryov after the 4 hikers in the den have been beaten so severely. Zolotaryov sustained beating to the head and flail chest caused by 5 broken ribs in two fracture lines. The camera was intact. The more I know the less it make sense.
- What was that made Zolotaryov take his camera, because they didn't seem to be under duress when the two went out of the tent, and
- What was on the camera after the incident
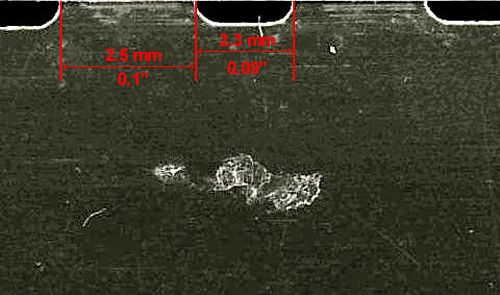
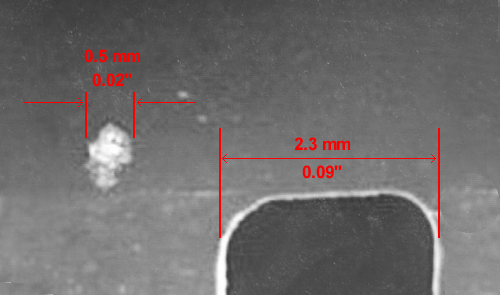
Psychic Photography
Valentin Yakimenko, who was a fellow student to the Dyatlov group and a member of the rescue team, presented at the Ural Federal University at the annual Dyatlov Conference 2015 examination of the films in the group cameras. He claims Zolotaryov grabbed his camera to take a picture of some lights in the sky. According to Yakimenko two of the negatives seem to depict a section of rocket or plane which may have broken off after a failed military experiment of possibly a two stage rocket launch.
Yakimenko says that the film was scrawled with Zolotaryov's name while non of the other films was tagged or labeled. We only lately speculate about the authorship of the photos on the films, so the fact that the only camera that was found on somebody's body was good enough reason to inscribe it. I don't think that reasons to allude there was special attention to that particular film.
"These photographs are a clear indication, of fallen angel/higher level demonic involvement, several of which, appear to capture, a partial physical manifestation, of a higher level, shape shifting demon... Yakimenko describes some of the photos as having 'A small, but very bright object', or being 'A bright little dot', which is typical of fallen angels and/or higher level demons, manifesting in orb form, that people mistakenly refer to as aliens or UFOs." Author Cora Hull Fallen Angels Exposed.
Please note that the images above, besides the first frame, are very small fragments of the actual photo. You can scale by the procket holes visible on scans 2 and 6.
At the 63 anniversary conference journalist Natalya Varsegova from Komsomolskaya Pravda showed what someone has made out of this scrap of film. The 3D model shows people around a fire, one of them carrying a gun. You can discuss on this board: Dyatlov Pass forum →
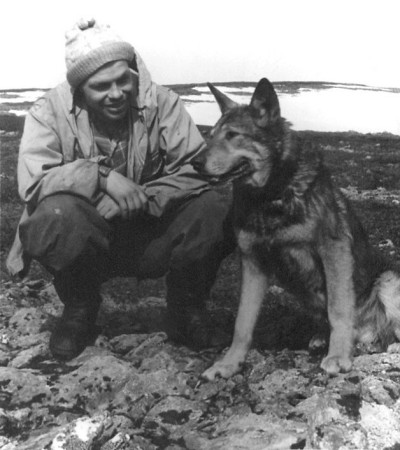
What was the name of the dog that found Zina?
We don't know what is the name of the dog on the photo, only that this dog was on Dyatlov Pass in May 1959, and the man on the photo is Askinadzi.
Theory 1
The name Alma is from Anna Matveeva's book "Dyatlov Pass" and later on Buyanov's book "Mystery of the Dyatlov group". Their source is an interview with Boris Leonidovich Suvorov from Mar 12, 1999:
"We got early in the morning. Kurikov was telling us where do we go today. The probe is a 3 meter stick with a hook at the end; push, twist, take out. We didn't get straight to the creek, but followed some pointers. For example melted things, broken branches, the dog Alma helped a lot. Passed many kilometers abreast. The expedition headed by Colonel Artyukov, and specifically led by students - Askenadzi. Artyukov decides to dig on suggestive objects."
Ed. note - I am citing the name of Colonel "Artyukov" as it is hand written by Suvorov. His name is Ortyukov.
Theory 2
Blinov's diary says that the name of the dog is Alta. Although in Cyrillic "t" and "m" can look alike in this case it's a clear "t". Blinov also underlined the name of the dog. See a scrap of his notebook:
"There is another entertainment in the camp - this is the service dog Alta. She understands every movement of her master, we are amused by her every day."
I am publishing a link to the transcript of Blinov's diary to have it handy.
Theory 3
In the case files when there is a reference to the search dogs they are always plural, and Karelin is explicitly saying two dogs. Victor Potyazhenko is also remembering flying to the pass with two dogs. It is probably possible to have two dogs on the search called Alma and Alta.
From the interview with Maya Piskareva:
– How many dogs?
– Two dogs, dogs were with dog handlers. Tails between their legs. They did not want to leave the helicopter. Later, dog handlers told me that the dogs felt in advance when the helicopter arrived, they were already preparing, waiting. They were afraid that they would be left there.
Is it true that local people were not allowed to graze their animals in the area?
Theory 1
From BBC podcast:
"But if the military was testing new weapons and there was a radiation leak, why did it only affect these nine students and why wasn’t the whole area contaminated?
Oleg (Arhipov) points out that it is a huge area, geographically, and few would have been aware of fallout in such a remote wilderness. Secondly, at the time of the students’ deaths, many animals and birds were found dead – and local people were suddenly banned from using water from wells. They had to bring in water from elsewhere.
Valery (Anyamov), the Mansi forest warden, told me that reindeer herders were banned from the area and hunting was not allowed for four years after the incident."
Theory 2
The animals were dying from necrobacteriosis (копытка) according to Bahtiyarov. The increase in animal deaths from this disease could be confused with the aftermath of a whatever they believed killed the hikers at the time, getting the facts backwards. It was rather a common epidemic that happened periodically. After all, Bahtiyarov himself knew the symptoms. If we need follow logically - if the wolves ate the meat of infected deer, then they themselves had to die. But no one talks about the wolves dying.
Read below about the ban on water sources.
Were hikers banned from going to the area after the incident?
Theory 1
Hikers were not allowed in the area after the incident.
Theory 2
There are reports of treks in August 1959 and August 1960 in the area of the pass. There were no restrictions on the use of water from rivers and springs. Hikers met with Mansi and saw their herds. In 1963, Yakimenko's expedition mounted the famous memorial plaque at the outlier rock. They also drank from the rivers.
It catches the eye that the first treks after the incident were not in winter, which speaks of concern regarding the area being dangerous in winter conditions, not in general. The first winter trek in the area after the incident with Dyatlov group is in 1970 when Evgeniy Sadakov dedicated to Dyatlov group the documentary "Wind, Rocks and Snow".
Histological analysis results of the first five bodies never made it to the case files
Theory 1
From BBC podcast:
"In the autopsy reports it says that fragments of the internal organs of the first five bodies were sent for chemical analysis. He unearthed a signed document stating the organs had been successfully delivered and were stored in a fridge. But as soon as the results were known, some people came to the laboratory and took the samples away, along with the paperwork."
Theory 2
Oleg Arhipov can not corroborate some of his statements. For example he was not friends with Lev Ivanov, and he received admission to the archive of Korotaev, not Lev Ivanov. About the histological samples there is a receipt that the samples of the first 5 bodies were received for testing by P.G. Chaschihina (case file vol.2-11)
This is as far as the paper trail goes. Arhipov then says he has information from anonymous witnesses that histological and chemical studies of the samples from the first 5 bodies were carried out in the Regional Bureau of Forensic Medicine laboratory. There are no supporting documents.
Soon after receiving the samples on Mar 10, the regional committee commission made a decision on the reasons for the death of the group to be a hurricane (special report of the CPSU). Since a criminal line of investigation was no longer viable the test were no longer needed.
Arhipov's take on the fact that there are no results from the testing is that the samples were seized by KGB officers who also kept guard around the hospital. This is all according to nameless witnesses. Allegedly, people who worked with Vozrozhdenniy and Gantz told him about this. Arhipov does not give the names or full record of the conversation.
Case files
- Slobodin autopsy report: "For chemical and histological analysis, parts of the internal organs and part of the pyramid of the temporal bone were removed." (case file 95-103)
- Doroshenko autopsy report: "Some organs from the body under examination have been taken for chemical and histological testing to the Regional Bureau of Forensic Medicine." (case file 104-111)
- Krivonischneko autopsy report: "For chemical and histological study, pieces of the internal organs of the body were removed." (case file 112-119)
- Dyatlov autopsy report: "For chemical and histological study, pieces of the internal organs of the body were removed." (case file 120-126)
- Kolmogorova autopsy report: "Parts of the internal organs were removed for chemical and histological analysis." (case file 127-134)
- Receipt for the acceptance of samples on March 10, 1959 by an employee of the Regional Bureau of Forensic Medicine laboratory P.G. Chaschihina (case files vol. 2 sheet 11)